Data Maturity Rubric: a roadmap to better data management
Robust data systems help organisations make better decisions and demonstrate accountability. For sustainability systems, effective data management enables performance tracking, risk management and responsiveness to evolving expectations. As demand from governments, businesses and civil society grows for credible insights, voluntary sustainability systems can meet these expectations through the valuable assurance, certification, and monitoring data they collect. ISEAL is helping its members improve the quality, accessibility and use of these data, supporting systems to meet external demands and prepare for the future.
A common framework for data maturity
To support members in their digital transformation, ISEAL has developed a Data Maturity Rubric (DMR) for sustainability systems and their partners to have a common language and criteria around data maturity. It was created through an iterative process with the ISEAL Data Community of Practice, including a pilot with seven members in 2023. It reflects practical needs and shared experiences across the community.
The rubric helps organisations assess how effectively they use data to generate insights and guide decision-making. While many data maturity models exist, the DMR provides a common language for sustainability systems and their partners to talk about their data systems. It helps them visualise and communicate the organisational maturity they need to achieve their sustainability goals.
The DMR is a self-assessment tool designed to motivate discussion and reflection across three themes: data culture, structure, and use. Each theme has an assessment focus and goal statement and contains six topics, laying out the key maturity elements for the theme.
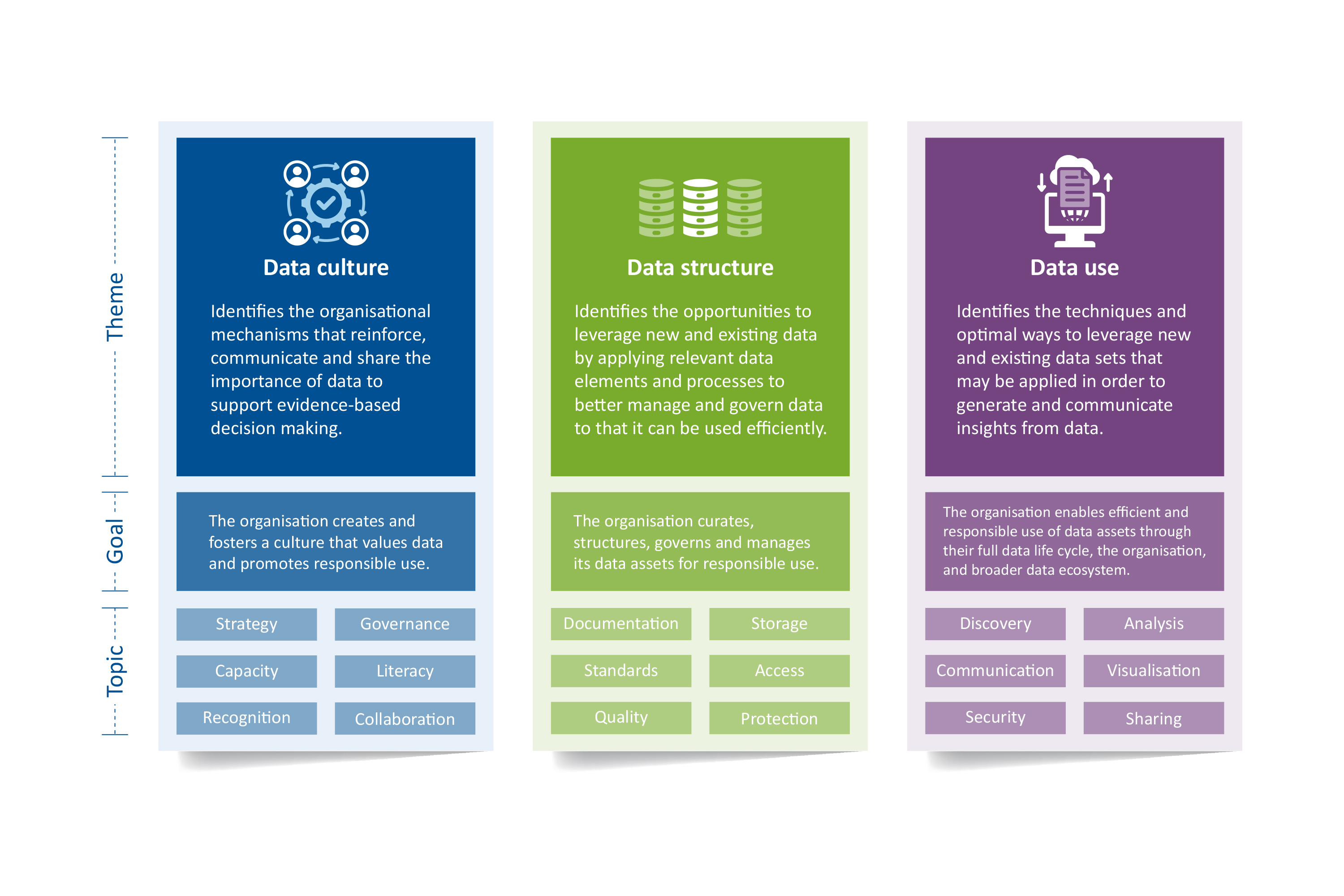
There are four possible levels of maturity for each of the eighteen topics, providing a guide to diagnose areas of strength and improvement:
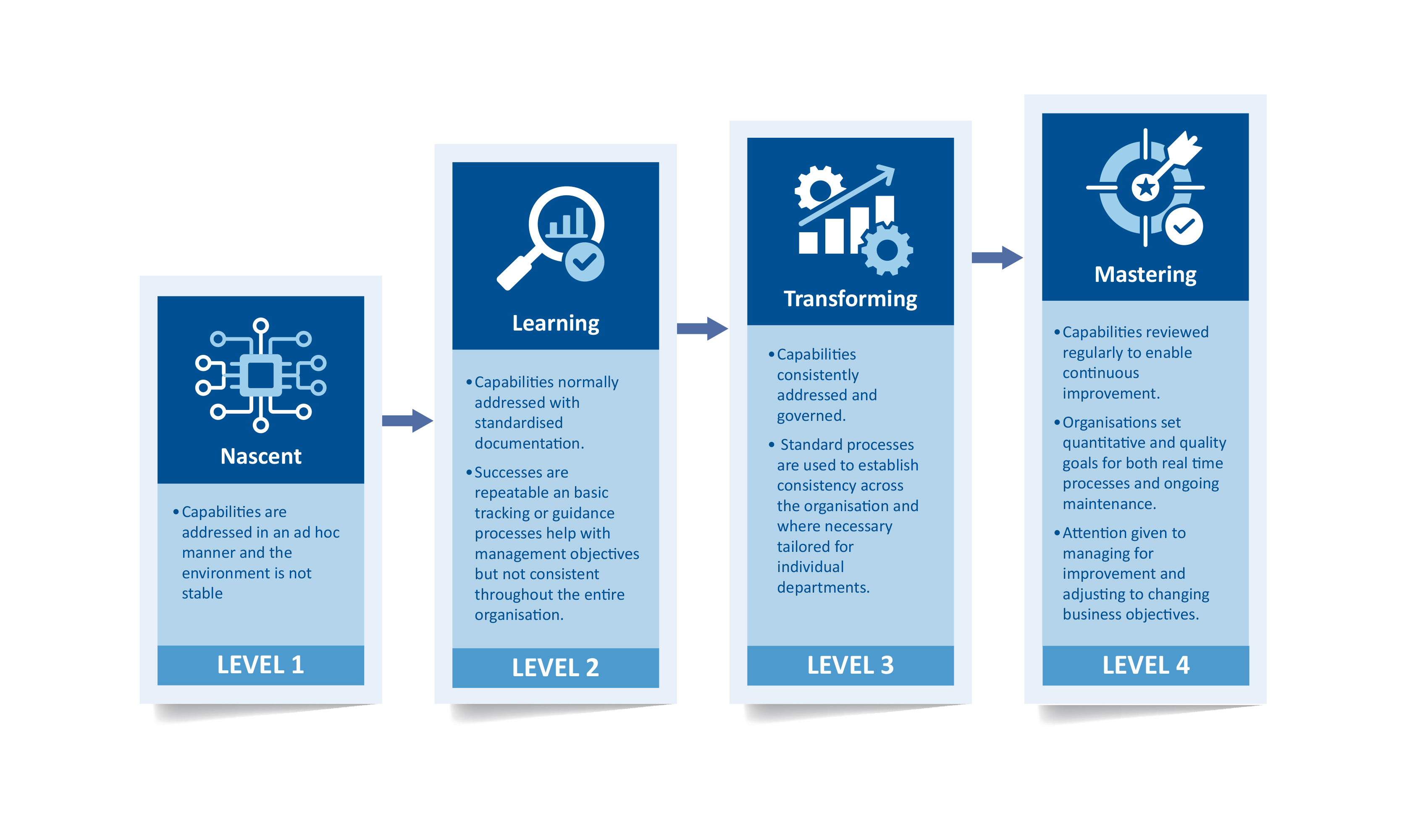
The full rubric, available to all ISEAL Community Members, includes definitions, goal statements, and guiding questions across the 18 topics, along with detailed descriptions of what maturity looks like for each topic.
Members who are using the rubric found that it enabled strategic resource allocation and fostered alignment across teams. By highlighting strengths and gaps, organisations could make informed decisions and track progress over time.

